Vertebroplasty (Pain Management Procedure)
Headed by Dr. Hemaxi Ambani
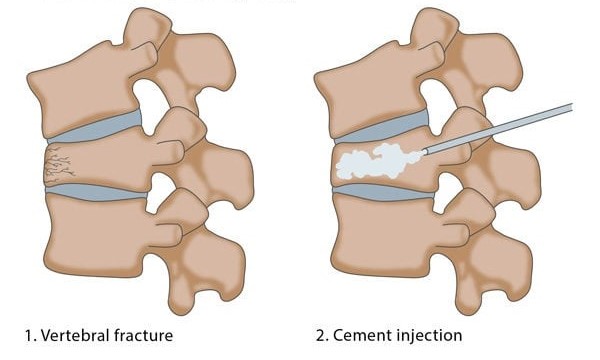
Vertebroplasty is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to treat compression fractures in the Pain specialist, typically caused by osteoporosis or cancer. It involves the injection of a special medical-grade cement into the fractured vertebra to stabilize it and relieve pain. Here's a detailed overview of the vertebroplasty procedure:
PRE-PROCEDURE PREPARATION
Before the procedure, the patient undergoes a thorough evaluation by a Doctor, which may include imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans to identify the location and extent of the vertebral fracture. Patients are advised to inform their doctors about any medications they are taking, as well as any allergies or medical conditions.
ANESTHESIA
Vertebroplasty is usually performed under local anesthesia, although some patients may receive sedation to help them relax during the procedure.
PROCEDURE STEPS
1. Patient Positioning: The patient is placed face down on the operating table. The skin over the area where the injection will be made is cleaned and sterilized.
2. Guidance Imaging: Using fluoroscopy (real-time X-ray guidance) or CT imaging, the Pain specialist locates the fractured vertebra with precision. This ensures accurate placement of the needle and cement.
3. Needle Insertion: A small incision (usually less than 1 cm) is made in the skin over the fractured vertebra. A hollow needle is then inserted through the skin and muscle and directed into the fractured vertebral body under continuous X-ray guidance.
4. Cement Injection: Once the needle is properly positioned, medical-grade bone cement (usually polymethylmethacrylate, PMMA) is injected into the fractured vertebra. The cement fills the spaces within the fractured bone, stabilizing it and providing support.
5. Monitoring: Throughout the injection process, the doctor monitors the flow of cement using imaging techniques to ensure it is distributed properly and doesn’t leak into surrounding tissues.
6. Needle Removal and Incision Closure: Once the cement has been injected, the needle is carefully removed, and the incision site is closed with adhesive strips or small sutures.
POST-PROCEDURE CARE
Recovery Room: After the procedure, patients are usually monitored in a recovery area for a short period.
Pain Management: Patients may experience immediate relief from pain, although some soreness at the injection site is common.
Activity: Most patients are able to resume light activities shortly after the procedure, but heavy lifting and strenuous activities should be avoided for a period of time.
Follow-up: Patients typically have a follow-up appointment with their doctor to monitor their progress and assess the effectiveness of the procedure.
BENEFITS OF VERTEBROPLASTY
Pain Relief: Vertebroplasty can provide rapid and significant relief from pain caused by vertebral compression fractures.
Improved Mobility: Stabilizing the fractured vertebra can improve mobility and quality of life.
Invasive: Compared to traditional open surgery, vertebroplasty is minimally invasive, with smaller incisions and a shorter recovery time.
RISKS & COMPLICATIONS
While vertebroplasty is generally safe, it does carry some risks, including:
- Cement leakage into surrounding tissues, which can cause nerve irritation or damage.
- Infection at the injection site.
- Allergic reactions to the cement or anesthesia.
- Rarely, damage to nearby blood vessels or nerves.